



Preethi Transplant center
What is Organ Donation?
Organ donation involves the removal of organs or tissues from a donor to be transplanted into a recipient. It is a life-saving procedure that can help those suffering from end-stage organ failure or serious health conditions.
How Does It Work?
Donation Types
Living Donation: An individual in good health can donate one of their kidneys, a part of their liver, or a portion of their lung to a recipient. Living donors typically undergo a thorough evaluation to ensure they are healthy enough to donate.
Deceased Donation: Organs are recovered from individuals who have recently passed away and whose organs are still viable for transplantation. Deceased donors are typically identified through donor registries or when a potential donor’s family agrees to donation.
Preethi Transplant center
Renal Transplantation Awareness
What is Renal Transplantation? Renal transplantation, commonly known as a kidney transplant, is a surgical procedure where a healthy kidney from a donor is placed into a person whose kidneys are no longer functioning properly. This procedure can significantly improve the quality of life and overall health for individuals with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD).
Why is it Needed? The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste products and excess fluids from the blood. When the kidneys fail, these functions are compromised, leading to the buildup of toxins and fluids in the body. A kidney transplant offers a chance to restore normal kidney function and eliminate the need for dialysis.
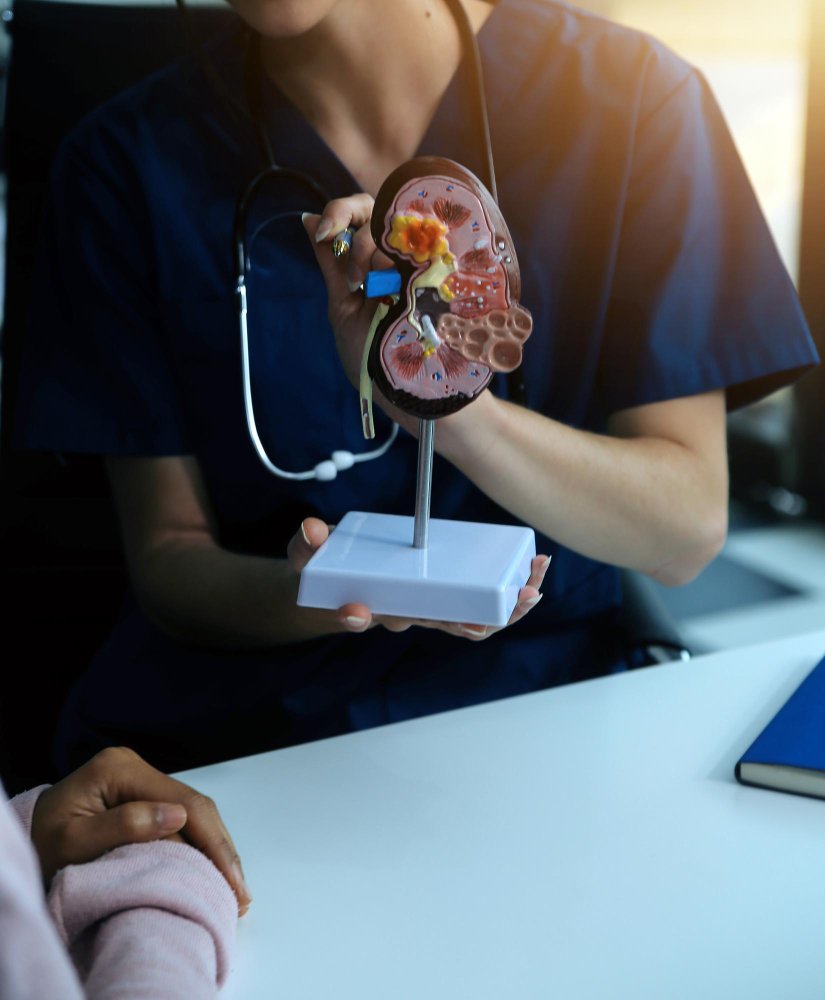
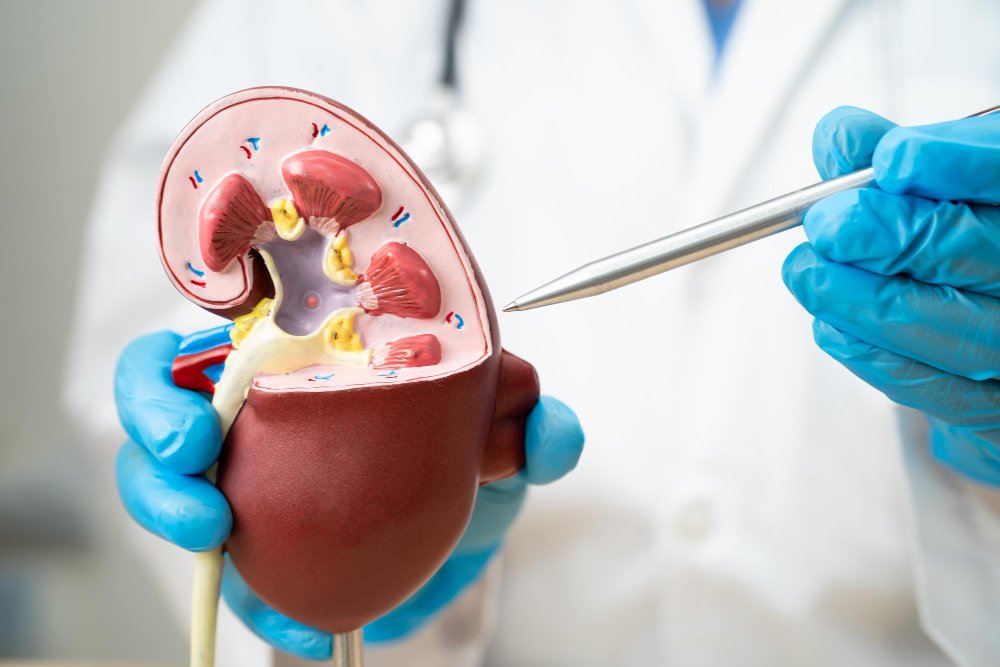
Benefits of Renal Transplantation
Improved Quality of Life
Many patients experience a significant improvement in their overall well-being & daily functioning.
Increased Life Expectancy
A successful kidney transplant can extend life expectancy compared to remaining on dialysis.
Freedom from Dialysis
Transplant recipients often enjoy a more flexible lifestyle without the need for regular dialysis treatments.
The Renal Transplant Process
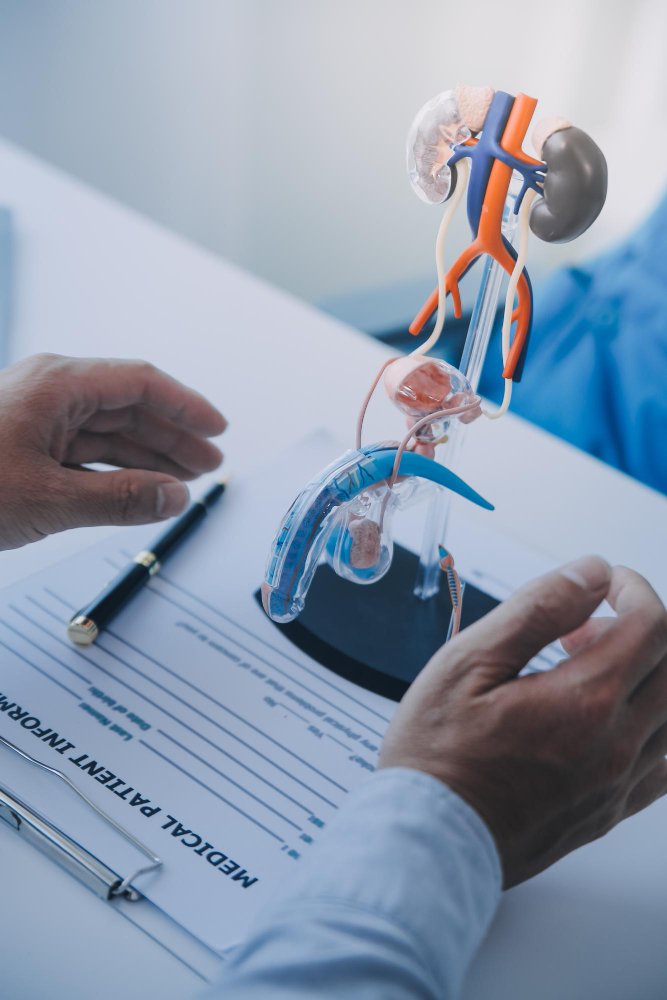
Pre-Transplant Evaluation
Medical Assessment: Patients undergo a thorough evaluation to determine if they are suitable candidates for a transplant.
Matching: Potential recipients are matched with compatible donors based on blood type, tissue type, and other medical criteria.
The Surgery
Procedure: The transplant surgery involves placing the donor kidney into the recipient’s abdomen and connecting it to the blood vessels and urinary tract.
Recovery: Post-surgery, patients require close monitoring and follow-up care to ensure the kidney is functioning properly and to manage any potential complications.
Post-Transplant Care
Medications: Recipients must take immunosuppressive medications to prevent organ rejection.
Regular Check-ups: Ongoing monitoring is essential to ensure the kidney is working well and to address any health issues.


Who Can Be a Donor?
Becoming a Kidney Donor
Living Donors: Individuals who are in good health and have compatible kidney function can donate one of their kidneys.
Deceased Donors: Organs from individuals who have passed away can also be used for transplantation.
